【質(zhì)譜】代謝組學(xué)工具 MZmine 2 manual指南
代謝組學(xué)工具 MZmine 2 manual指南
菜鳥(niǎo)博士Caesar
MZmine 2 installation
Download the MZmine distribution (ZIP file) and unpack it into a folder of your choice.
That’s all.
3. Starting MZmine 2
3.1. Starting in GUI mode
A startup script is provided for MS Windows (startMZmine_Windows.bat), Mac OS X (startMZmine_MacOSX.command) and Linux (startMZmine_Linux.sh) environments. Start MZmine in the GUI mode by running this script. Please note that the amount of memory used by the program is limited by the value of the HEAP_SIZE parameter in the startup script. The default value is set to half
of your physical RAM. If you wish to use more RAM for MZmine 2, please edit the startup script.
3.2. Starting in batch mode
If the?startMZmine...?script is supplied with a command line parameter, this parameter is treated as a batch queue file (see Batch mode). In such case MZmine is started as a command-line application and the batch file is loaded into the batch mode module and executed. Upon finishing the whole batch, MZmine will automatically quit. This allows to integrate MZmine into scriptable work flows. Note that the first step of the batch should be always either the “Raw data import” module or
the “Project load” module, otherwise MZmine will have no data to process.
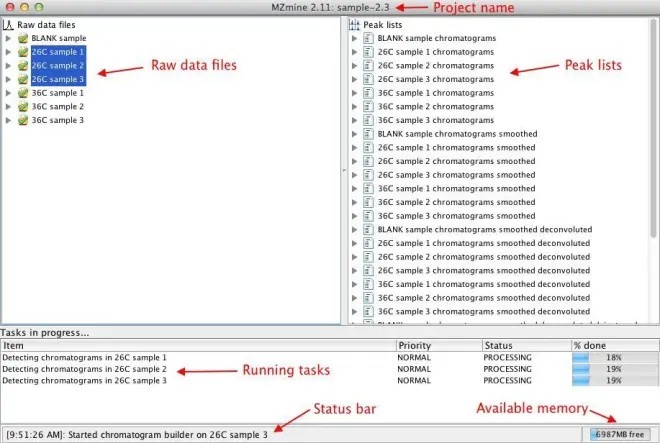
4. MZmine 2 desktop
The following screenshot describes the components of the main MZmine 2 window:
The order of the raw data files and peak lists in the project tree may be changed using mouse
(drag & drop).
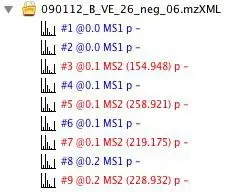
If you expand the raw data files in the left section of the main window, you will see a list of scans in the file. MS scans are shown in blue, while MS/MS scans are shown in red. Each scan is annotated with its sequential number (#), retention time in minutes (@), MS level (for MS/MS scans the precursor m/z is also shown), type of spectrum (p?= profile,?c?= centroid,?t?= thresholded), and
polarity of ionization (+?= positive,?-?= negative,???= unknown).
Page 7
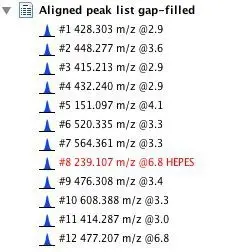
Similarly, expanding the peak list in the right section of the project window will show its individual rows with their ID (#), m/z value and retention time (@). Rows that have identity information
attached are displayed in red and their name is also shown.
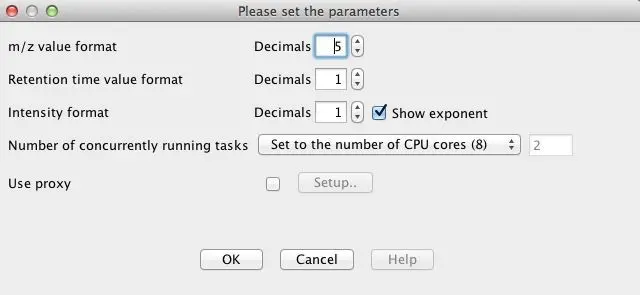
4.1. Number formatting
Formatting of the m/z, retention time and intensity values may be modified in the dialog
activated by the Project represented in minutes./Set preferences menu item. Note that the retention time is always
5. Data processing
5.1. Raw data import
MZmine 2 can read and process both low-resolution (unit mass) and high-resolution (exact mass) data in both continuous and centroided modes, including fragmentation (MSn) scans. Supported data formats are:
mzML?(mzML version 1.0 and 1.1)
mzXML?(mzXML versions 2.0, 2.1 and 3.0)
mzData?(mzData versions 1.04 and 1.05)
NetCDF?(no MSn data support)
Thermo RAW?(native data format)
Waters RAW?(native data format)
The support for native data formats is implemented using a small external program, which runs only on Windows. On Linux or other platforms, MZmine will attempt to execute the external program through the Windows emulator Wine (http://www.winehq.org), so you can try to install it.
5.2. Setting sample parameters
Parameters can be added to the MZmine project and their values can be set for each sample individually. These parameters can later be used in further stages of data processing, for example in
the Intensity plot. The addition of the parameters to the project is done in the following steps:
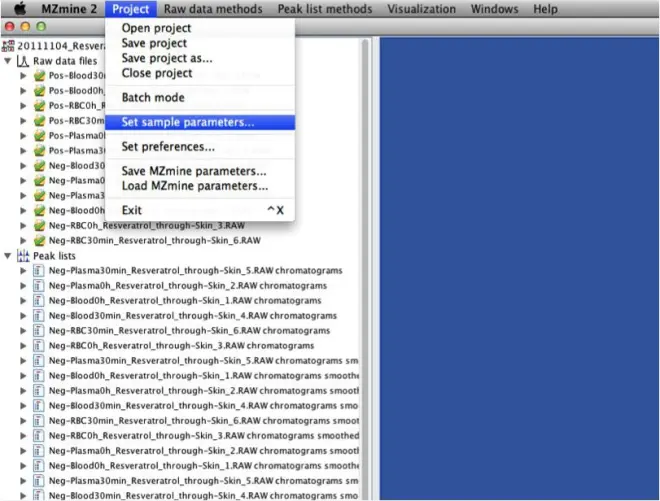
1. Open the Set sample parameters dialog
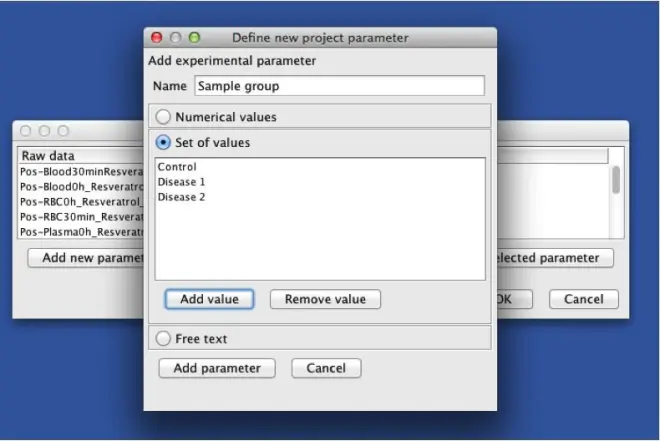
2. Add a new parameter. Each parameter can have numerical values, text values, or a set of
defined values (options).
Page 10
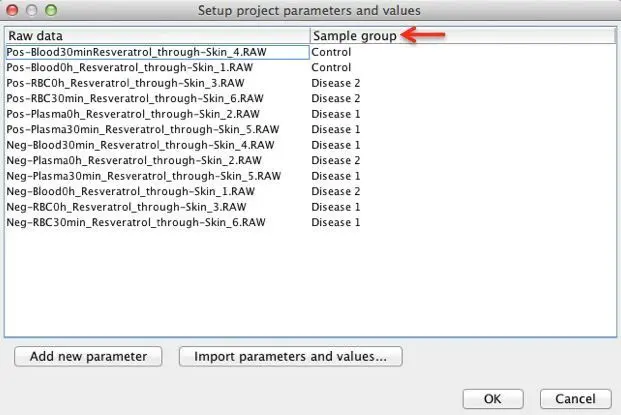
3. Set the parameter value to each sample
The parameters and values can also be imported from a comma-separated (CSV) file. The
format of the input CSV file is as described below.
First column of the comma-separated file must contain file names matching to names of raw
data files opened in MZmine. Each other column corresponds to one project parameter.
First row in the file must contain column headers. Header for the first column (filename) is ignored but must exists. Rest of the column headers are used as names for project parameters. All column names in the file must be be unique. If main dialog already contains a parameter with the same name, a warning is shown to the user before overwriting previous parameter. The type of the imported parameter is decided according to the following rules:
If all values in a column (except column header on the first row) are numeric, then the parameter type is set to numerical.
If there are at least some duplicate strings among values for a parameter, then the parameter type is “Set of values” and possible parameter values are all unique strings.
Otherwise it is a free text parameter.
5.3. Data processing workflow
The typical workflow for processing mass spectrometry data using MZmine 2 consists of the
following steps (note that some of these steps are optional and may be skipped). The bold font indicates the name of the corresponding item in the MZmine application menu.
Raw data import
(Optional)?Raw data methods / Filtering
Peak detection, using one of the available methods
Generation of mass lists (detected ions) for each scan using?Mass detection, followed by?FTMS shoulder peaks filter?(optional), followed by detection of chromatograms using the?Chromatogram builder, followed by?Smoothing?(optional), followed by separation of individual peaks in the chromatograms using the?Chromatogram deconvolution?module
2D peak detection using the?GridMass?module
Peak list generation from precursor ions of MS/MS scans using the?MS/MS peaklist builder?module, followed by the?Peak extender?module
Targeted peak detection?from a given list of target ions
Removing of isotopes using the?Isotopic peak grouper?module
(Optional)?Identification?of fragments, adducts and peak complexes
(Optional)?Normalization?of retention time using the?Retention time normalizer Alignment?using the?Join aligner?or?RANSAC aligner
(Optional)?Gap filling?using the?Peak finder?or?Same RT and m/z range gap filler?(Optional)?Normalization?of peak heights/areas using the?Linear normalizer?or?Standard compound normalizer
(Optional)?Identification?using?Custom database search,?Online database search,?Formula prediction, etc.
Data analysis,?Export,?Visualization?etc..
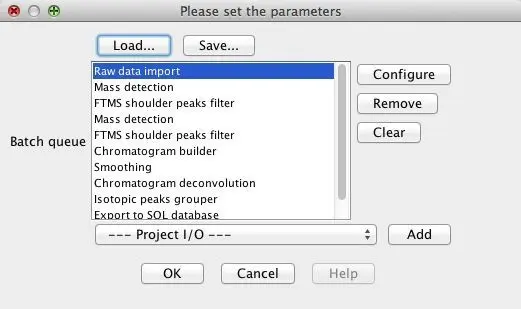
5.4. Batch mode
MZmine 2 has the option to run multiple data processing methods in batch mode. The following figure shows the batch mode setup dialog, where the user can setup the individual batch steps. At the moment of adding a new step, the corresponding parameter setup dialog appears. It is also possible to change the steps or the parameters of each step with "Configure" and "Remove" buttons. The contents of the batch queue can be saved to a XML file and later restored by clicking the
“Load..” button.
6. Documentation for individual modules
Please refer to MZmine’s internal Help for the documentation of individual modules and
algorithms. Each parameter setup dialog has a Help button as shown below:

